Dermatology encompasses many conditions that can affect the appearance and health of the skin. These conditions can be temporary or chronic, mild or severe, and are caused by many factors, including genetics, environmental influences, allergies, infections, and lifestyle choices. Common skin conditions include acne, eczema, psoriasis, rosacea, and hives. Each condition has its own unique symptoms and requires a unique approach to care.
Common skin conditions
- Acne: This is a skin condition characterized by the appearance of blackheads, whiteheads, papules or cysts. Acne often affects areas such as the face, neck, shoulders, chest and back. Treatment options include topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide products, antibiotics to control inflammation and hormonal therapy for those with hormonal deficiencies.
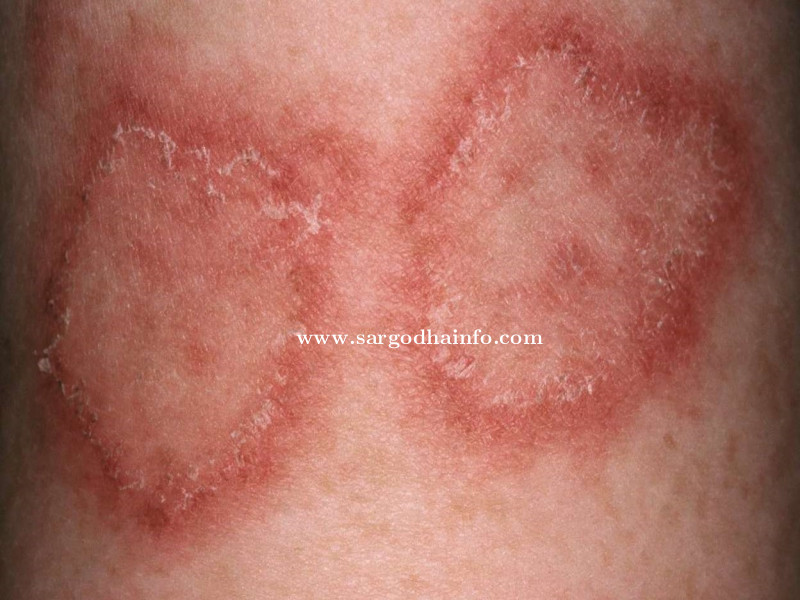
- Eczema: Also known as atopic dermatitis, eczema looks like itchy patches that can appear red or brown on dark skin. It usually occurs in response to an allergen or irritant and can be worsened by stress or environmental factors. Treatment usually includes using moisturizers to keep the skin moist and topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Psoriasis: This autoimmune disease causes skin cells to grow unexpectedly, ensuing in scaly, silvery scales. Psoriasis generally influences areas inclusive of the scalp and elbows, but can arise anywhere at the frame. Treatment may encompass medications (which include corticosteroids), phototherapy (light remedy), and, for extra extreme cases, medicines.
- Rosacea: A persistent circumstance that typically affects the face; can encompass spicy ingredients, alcohol, sun publicity and pressure. Treatment usually consists of topical medicines such as metronidazole or azelaic acid and, in greater intense cases, oral antibiotics.
- Urticaria (hives): Symptoms as a result of skin sicknesses that are in general itchy; antihistamines are regularly used to relieve symptoms.
- Cold Sores: Cold sores are caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) and seem as a rash across the mouth. They are contagious and typically resolve inside some weeks, but they can reoccur due to triggers including stress or infection.
- Blisters: Fluid-filled pockets in the skin caused by friction or burns; they protect the tissues while they heal.
- Actinic keratosis: A pre-existing condition caused by sun damage that causes hardening of the skin in sun-exposed areas and should be monitored for the potential for skin cancer.
- Carbuncles: These are boiling that form on the skin due to infection. They need treatment, especially if they are accompanied by fever.
- Latex allergy: This serious allergic reaction manifests itself as a rash after contact with latex products; if you have difficulty breathing, you should seek immediate medical attention.
Health Care Strategies
Good health management usually includes a combination of medication and lifestyle changes:
- Consult a doctor: Get a correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
- Cosmetics: For example, creams or ointments may be prescribed in a case.
- Oral medications: When topical medications are not effective.
- Regular monitoring: Keeping track of any changes in symptoms can help prompt intervention if the
condition worsens.
Lifestyle changes:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Use gentle skin care products that do not contain harsh chemicals.
- Protect yourself from the sun with sunscreen.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques that will help reduce the occurrence of conditions such as eczema or itching.
In summary, understanding the various aspects of skin and their treatment is essential to developing effective management and care tailored to the needs of the individual.